Chapter#21 IO : File and Directory
- Files and Directories
- Unix file IO
- Links
- Mount
Files and Directories
Storage Virtualization
File : read/write가능한 linear array of bytes
- content : creator에 의해 만들어짐 e.g. text/binary
- inode number로 identified됨 (pid와 유사)
Directory : file과 directories를 묶기 위한 special file
- content : list of (user-readable name, inode #) pairs를 가짐
- hierarchical oraganization ( tree, acyclic-graph, graph )
- inode number로 indentififed됨
트리구조이므로 최상위 directory는 root ( '/'로 나타냄 )
Pathname :
- absolute pathname : /home/~~/~~~
- relative pathname : ~~/~~~
Working Directory :
- 모든 process는 working directory가 있다 ( pwd로 확인 )
Home Directory :
- log in된 origin directory
Unix File : normal file만 아니라 peripheral device와 inter-process communication channels도 file로 간주
- /dev/stdin, /dev/stdout, /dev/rmt0 (tape device), /dev/sda2 (disk partition), /dev/tty2 (terminal), /proc (kernel data structure) 등등
- FIFO, PIPE, SOCKET
- 모두 고유 inode number 가짐
Unix Directory :
- (user-readable name, inode #) pairs를 가짐
- directory의 각 entry는 file or directories로 간주됨
- 마찬가지로 고유 inode number 가짐
Ownership
- 각 file은 particular user의 소유이다
- Owner은 file의 permission을 설정할 수 있다
Permissions
- 누가 어떻게 file에 access할 수 있는지 설정

Superuser(or administrator) : rwx에 상관없이 모든 파일에 access 가능
Unix file IO
Creaing Files
int fd; // file descriptor
if ((fd = open("foo", O_CREAT | O_WRONLY | O_TRUNC)) < 0){
perror("open");
exit(1);
}O_CREAT : creat file
O_WRONLY : only write
O_TRUNC : make the file size zero ( = remove any existing content )
open() returns file descripter : an integer, used to access files
- return -1 : perror("open");
Closing Files
int fd; // file descriptor
int retval; // return value
if((retval = close(fd)) < 0){
perror("close");
exit(1);
}
Reading and Writing Files
1. open() call
2. 반복적으로 read(), write() call
3. close() call
strace 명령어를 통해 어떤 call들이 이뤄졌는지 확인 가능
open(file descriptor, flags) : return file descriptor. 0/1/2 = stdin/stdout/stderr
read(file descriptor, buffer pointer, size of buffer) : return 읽은 byte 수
write(file descriptor, buffer pointer, size of buffer) : return 쓴 byte 수
current offset : read/write가 현재 어디서 시작할지 나타냄
- Implicitly : read/write N bytes를 하면 current offset += N
- Explitly : lseek()
off_t lseek(int fileds, off_t offset, int whence);fildes : file descriptor
offset : position the file offset to particular location
whence : determine how seek is performed
- SEEK_SET : 0 + OFFSET
- SEEK_CUR : CUROFFSET+OFFSET
- SEEK_END : ENDPOINT + OFFSET
Renaming Files
rename(char* old, char* new)
ex) > mv foo bar
ex) rename("foo.txt.tmp", "foo.txt");
Getting Information About Files
stat(), fstat() : show file metadata
struct stat {
dev_t st_dev; /* ID of device containing file */
ino_t st_ino; /* inode number */
mode_t st_mode; /* protection */
nlink_t st_nlink; /* number of hard links */
uid_t st_uid; /* user ID of owner */
gid_t st_gid; /* group ID of owner */
dev_t st_rdev; /* device ID (if special file) */
off_t st_size; /* total size, in bytes */
blksize_t st_blksize; /* blocksize for filesystem I/O */
blkcnt_t st_blocks; /* number of blocks allocated */
time_t st_atime; /* time of last access */
time_t st_mtime; /* time of last modification */
time_t st_ctime; /* time of last status change */
};ex) > stat file
indoe structure : disk에 저장된 file system에 의해 관리된 type of information
Removing Files
ex) > rm file
ex) unlink("file")
Making Directoreis
ex) > mkdir dir
ex) mkdir("dir", 0777)
처음에 ls하면 . (itself)와 .. (parent)를 가짐
Reading Directories
// sample code of ls
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
DIR *dp = opendir("."); // open current directory
assert(dp!=NULL);
struct dirent *d;
while((d = readdir(dp)) != NULL){ // read one directory entry
print("%d %s\n", (int) d->d_ino, d->d_name);
}
closedir(dp); // close current directory
return 0;
}struct dirent {
char d_name[256]; /* filename */
ino_t d_ino; /* inode number */
off_t d_off; /* offset to the next direct */
unsigned short d_reclen; /* length of this record */
unsigned char d_type; /* type of file */
}
Deleting Directories
rmdir() : empty directory인 경우만 가능. 아니면 fail
Links
Hard Links
link(old pathname, new one)
- same file을 refer함
- ex) > ln file file2
작동 :
- create another name in directory
- refer same inode number of origin
제거(remove file) :
- 해당 file inode를 refer하는 파일 개수를 count
- unlink() call되면 count 1 감소
- count가 0이 되면, 실질적으로 inode와 data block 제거
여러 file system을 사용하는 경우 문제 발생할 수 있음
Symbolic Links(Soft Link)
hard link는 다른 partition에 파일 생성 불가
ex) > ln -s file file2
새 inode 값을 가지며 content는 원본 file pathname ( = 4 bytes, longer pathname -> larger bits )
-> Dangling reference : 원본이 지워지면 link가 남을 수 있음 (trash)
Mount
mkfs tool : make a file system
- 빈 파일 시스템 씀. root에서 시작
- input : device (e.g. /dev/sda1), file system(e.g. ext3)
mount()
- 기존 directory를 mount point를 가리키게 함
ex) > mount -t ext3 /dev/sda1 /home/users
= /home/users/ 는 /dev/sda1의 root를 가리킴
 |
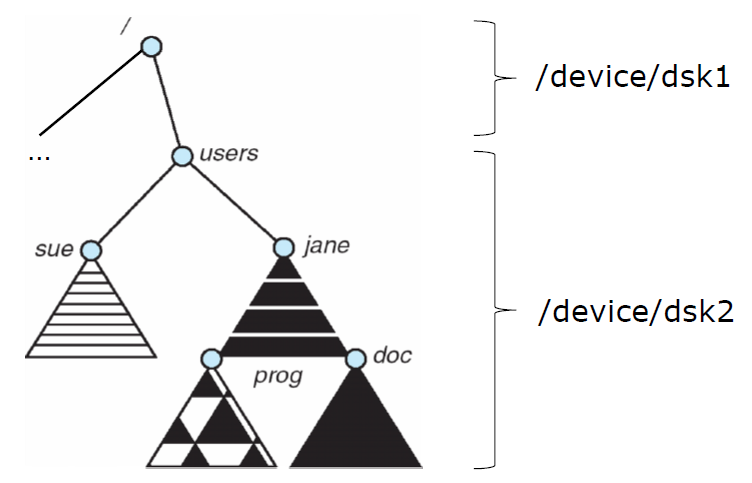 |
ex)
/dev/sda1 on / type ext3 (rw)
proc on /proc type proc (rw)
sysfs on /sys type sysfs (rw)
/dev/sda5 on tmp type ext3 (rw)
/dev/sda7 on var /vice/cache type ext3 (rw)
tmpfs on / dev shm type tmpfs (rw)
AFS on /afs type afs (rw)ext3 : standard disk-based file system
proc : file system for accessing information about current process
tmpfs : file system for temporary files
AFS : distributed file system
학교 강의를 토대로 개인 공부 목적으로 작성되어 오타가 및 오류가 있을 수 있으며, 문제가 될 시 삭제될 수 있습니다.
'Study > 운영체제' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Chapter# 23 Fast File System (0) | 2021.12.11 |
|---|---|
| Chapter#22 File System Implementation (0) | 2021.12.11 |
| Chapter#20 Flash-based SSDs (0) | 2021.12.10 |
| Chapter#19 I/O : HDD and RAID (0) | 2021.12.10 |
| Chapter#18 I/O Device (0) | 2021.12.10 |



